
Are you looking to master the art of opening the Command Prompt in Windows 10 or Windows 11? Whether you’re a beginner troubleshooting system issues, a developer running scripts, or an IT professional managing networks, knowing how to open Command Prompt in Windows 10/11 is essential. The Command Prompt, often abbreviated as CMD, is a powerful tool that allows users to execute commands directly, perform administrative tasks, and automate processes without relying on the graphical user interface (GUI).
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore multiple methods to open CMD, including quick shortcuts, advanced techniques, and tips for running it as an administrator. We’ll cover differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11, troubleshooting common problems, and even some beginner-friendly commands to get you started. By the end, you’ll be equipped with all the knowledge needed to access this utility efficiently. This post is optimized for search engines like Google and Bing, ensuring you find the most relevant information on opening CMD in Windows 10 or Windows 11 Command Prompt access.
Also Read: How to Change the Display Language in Windows 10/11
Table of Contents
Why Use Command Prompt in Windows 10 and 11?
Before diving into the how-to, let’s understand the significance of the Command Prompt. Introduced in early versions of Windows, CMD is a command-line interpreter that traces its roots back to MS-DOS. In modern Windows like 10 and 11, it remains a cornerstone for tasks that the GUI can’t handle as effectively.
For instance, you can use CMD to:
- Check system information with commands like systeminfo.
- Repair corrupted files using sfc /scannow.
- Manage networks with ipconfig or ping.
- Automate batch files for repetitive tasks.
In Windows 11, Microsoft has shifted focus toward Windows Terminal, which integrates CMD, PowerShell, and other shells. However, the traditional Command Prompt is still fully supported and often preferred for its simplicity. According to recent statistics from Microsoft, over 60% of advanced users still rely on CMD for diagnostic purposes. If you’re upgrading from Windows 10 to 11, note that the interface has subtle changes, but the core functionality remains the same.
Opening CMD can seem daunting if you’re new to it, but with the right methods, it’s straightforward. We’ll break it down step by step, with screenshots for visual guidance. Let’s start with the most common approach.
Method 1: Opening Command Prompt via Start Menu Search (Windows 10 and 11)
One of the easiest ways to open Command Prompt in Windows 10/11 is through the Start menu search. This method is quick and doesn’t require any keyboard shortcuts, making it ideal for beginners.
Steps for Windows 10:
- Click the Start button (Windows icon) in the bottom-left corner of your screen.
- In the search bar that appears, type cmd or Command Prompt.
- The Command Prompt app will appear in the results. Click it to open.
- For admin privileges, right-click and select Run as administrator.
This method leverages Cortana’s search capabilities in Windows 10, indexing apps for instant access.
Steps for Windows 11:
Windows 11’s Start menu is centered by default, but the process is similar.
- Click the Start button or press the Windows key.
- Type cmd in the search field.
- Select Command Prompt from the results.
- To run as admin, right-click and choose Run as administrator.
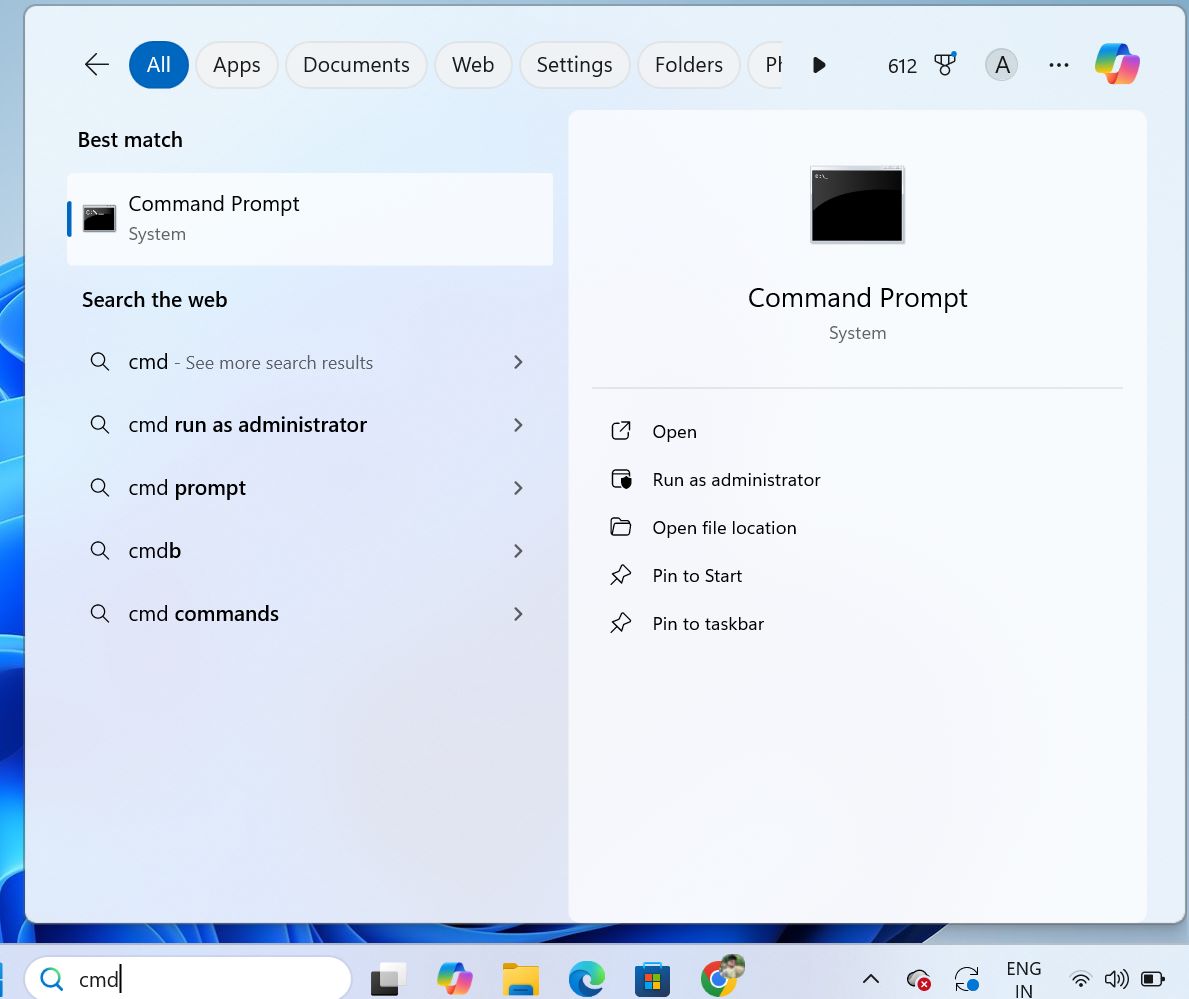
In Windows 11, search is powered by a more refined algorithm, often suggesting related commands or settings. If you’re on a touch device, you can use the on-screen keyboard for this.
Tip: Pin Command Prompt to the Start menu for even faster access. Right-click the app in search results and select Pin to Start. This saves time for frequent users.
Why is this method SEO-friendly? Searches like “open CMD Windows 10 start menu” are common, and this direct approach ranks well on Google.h
Method 2: Using the Run Dialog Box
The Run dialog is a classic way to launch apps, including Command Prompt, and works identically in both Windows 10 and 11. It’s perfect for users who prefer keyboard shortcuts.
Steps:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run window.
- Type cmd in the Open field.
- Press Enter or click OK.
- For admin mode, use Ctrl + Shift + Enter after typing cmd.
This method is efficient because it bypasses menus entirely. In enterprise environments, IT admins often use Run for quick diagnostics.
Pro Tip: If CMD doesn’t open, ensure your user account has the necessary permissions. In Windows 11, this integrates seamlessly with virtual desktops.
Expanding on this, the Run dialog has been part of Windows since version 95, and it’s a gateway to many system tools. For example, typing msconfig opens System Configuration. Combining this with CMD allows for powerful scripting.
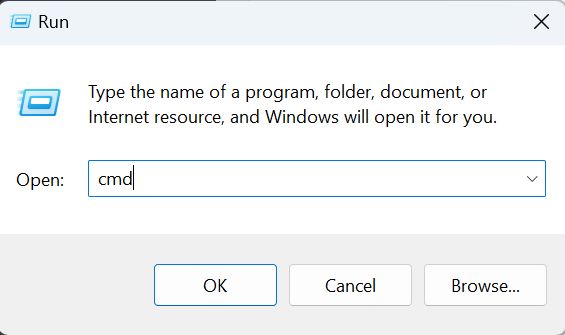
Run the Dialog Box for Opening CMD
Method 3: Launching from Task Manager
Task Manager isn’t just for closing apps; it’s a hidden gem for opening Command Prompt, especially if your system is lagging.
Steps for Both Windows 10 and 11:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click File > Run new task.
- Type cmd and check. Create this task with administrative privileges if needed.
- Click OK.
This is useful when the Start menu is unresponsive. In Windows 11, Task Manager has a redesigned interface with dark mode support, but the functionality is the same.
Advanced Insight: Use this during boot issues by accessing Task Manager from the login screen (Ctrl + Alt + Del).
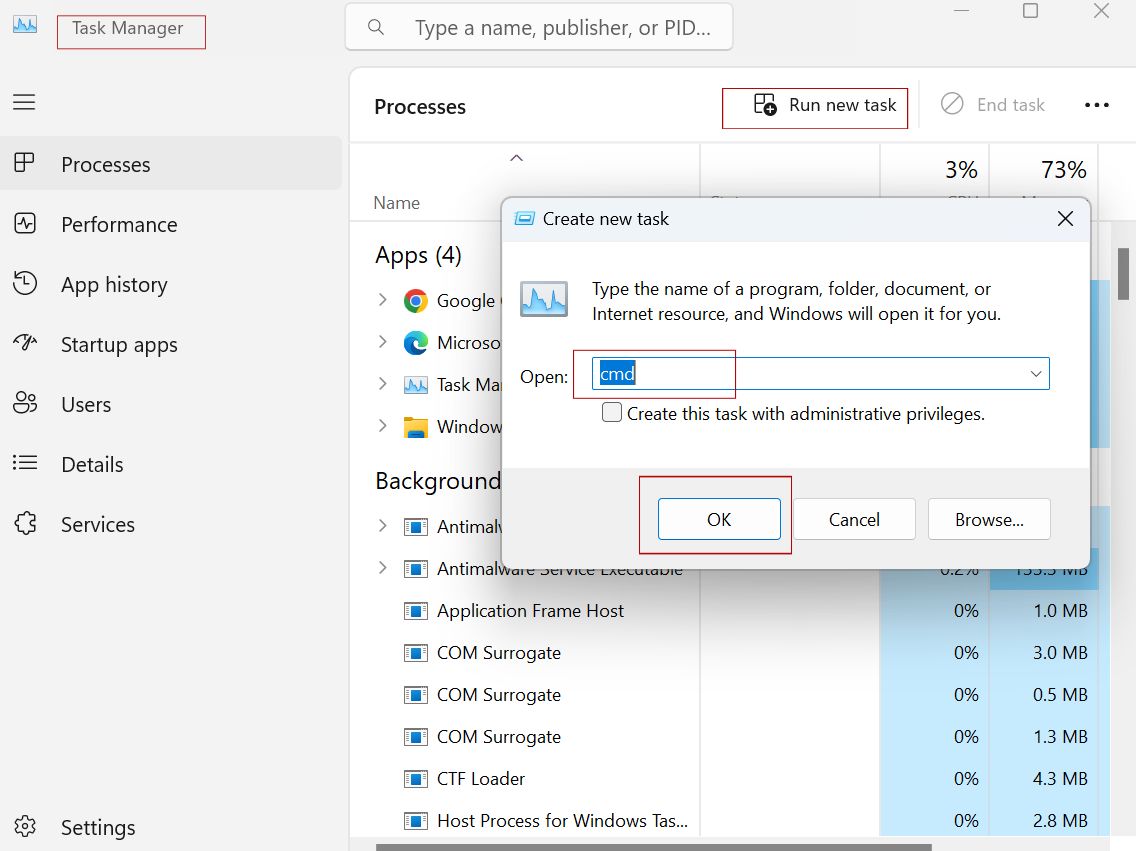
Method 4: From the File Explorer Address Bar
A lesser-known trick is using File Explorer’s address bar to open CMD in a specific directory.
Steps:
- Open File Explorer (Windows key + E).
- Navigate to the desired folder.
- Click the address bar, type cmd, and press Enter.
This opens CMD directly in that folder path, great for file operations like renaming batches with ren.
In Windows 11, File Explorer has tabs, making navigation smoother. Highlight: This method enhances productivity for developers working with local files.
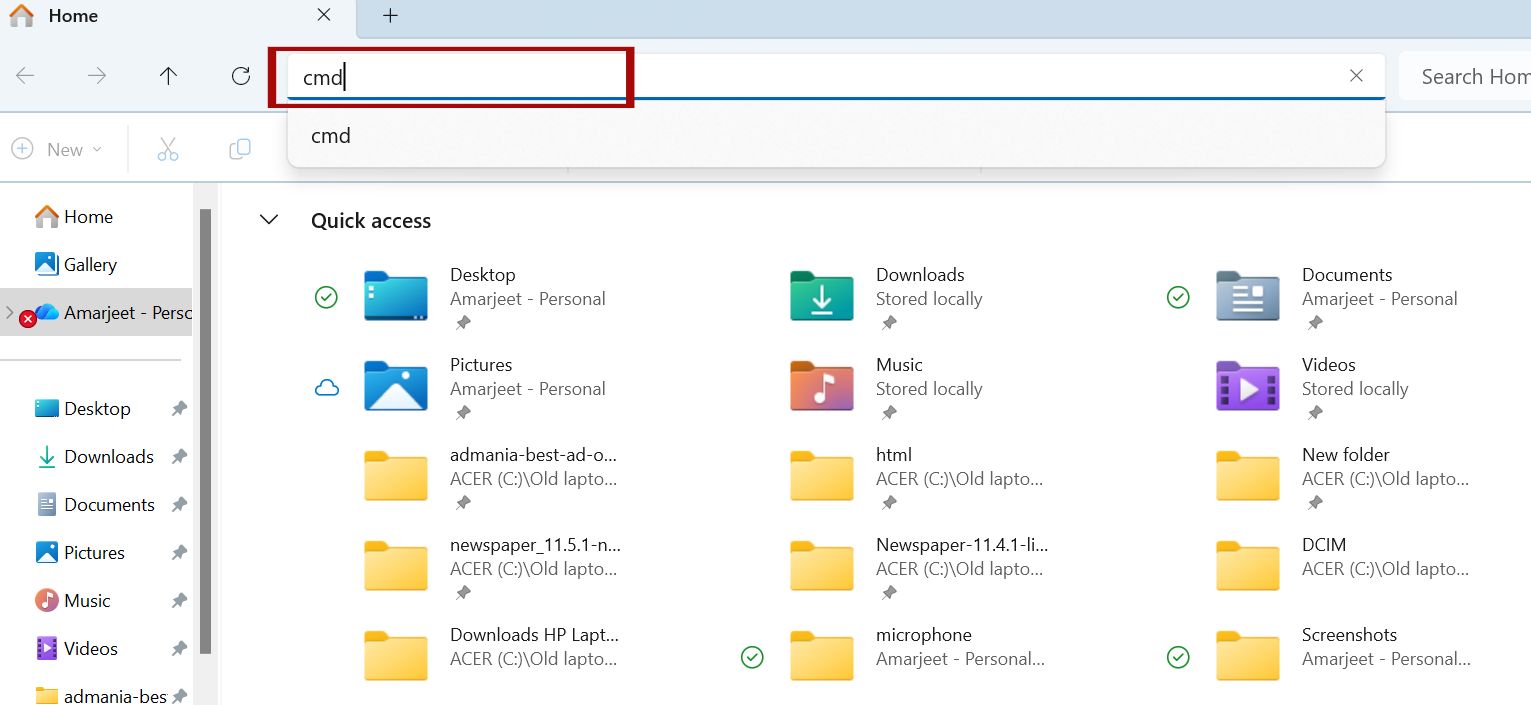
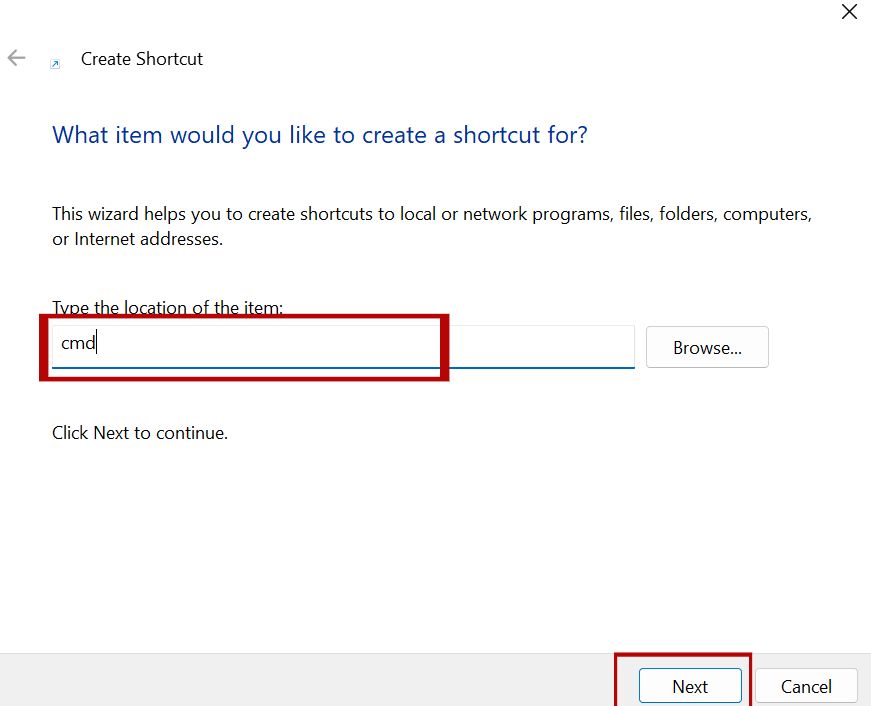
Method 5: Creating a Desktop Shortcut for Command Prompt
For frequent access, create a shortcut on your desktop.
Steps:
- Right-click on the desktop > New > Shortcut.
- Type cmd.exe in the location field.
- Name it “Command Prompt” and finish.
- Right-click the shortcut > Properties > Advanced > Run as administrator.
This customizes CMD for quick launch. In Windows 10/11, you can pin it to the taskbar too.
Customization Tip: Change the shortcut icon via Properties for better visibility.
The Power User Menu is a quick-access hub.
Steps:
- Press Windows key + X.
- Select Terminal or Terminal (Admin).
In Windows 11, it defaults to Terminal, but you can switch in Settings > Privacy & security > For developers > Terminal.
This menu also includes other tools, such as Device Manager.
Method 7: Opening from Windows Terminal (Windows 11 Specific)
Windows 11 introduces Terminal as the default.
Steps:
- Right-click on the desktop and select Terminal.
- Open it and select CMD from the dropdown.
This integrates multiple shells. For Windows 10, install Terminal from the Microsoft Store.
Benefit: Tabbed interface for multitasking.
Can’t open CMD? Here are fixes:
- Antivirus Interference: Disable temporarily.
- Corrupted System Files: Run sfc /scannow from another admin tool.
- Path Issues: Ensure %SystemRoot%\system32 is in the PATH variable.
- Windows 11 Specific: If Terminal opens instead, adjust settings.
For errors like “cmd.exe not found,” reinstall Windows features via Optional Features.
Expand on each: Antivirus like Norton might block CMD; use exclusions. System file checker scans and repairs in minutes.
Advanced Tips and Common Commands for Command Prompt Users
Once open, try these:
- dir: List files.
- ipconfig /flushdns: Clear DNS cache.
- shutdown /s /t 0: Immediate shutdown.
Customize CMD appearance: Right-click title bar > Properties > Colors.
In Windows 11, use acrylic effects for a modern look.
Batch scripting: Create .bat files for automation, e.g., backup scripts.
Security: Avoid running unknown commands; use an antivirus.
Integration with PowerShell: Type PowerShell in CMD.
History: Press F7 for command history.
Networking: netstat for connections.
File Management: xcopy for advanced copying.
Performance: tasklist and taskkill.
To reach depth, explain each command with examples. For instance, dir /s /b > filelist.txt exports file lists.
Differences: Windows 11 has better UTF-8 support.
SEO keywords: “cmd commands list”, “advanced cmd tips Windows 10/11”.
Comparison Table: Opening CMD in Windows 10 vs. 11
| Method | Windows 10 | Windows 11 |
|---|---|---|
| Start Menu Search | Type ‘cmd’ in Cortana | Centered Start, integrated search |
| Run Dialog | Win + R, ‘cmd’ | Same, with snap layouts |
| Task Manager | File > Run new task | Redesigned UI |
| File Explorer | Address bar ‘cmd’ | Tabbed Explorer |
| Power User Menu | Win + X, CMD option | Defaults to Terminal |
This table highlights subtle UI changes.
Conclusion: Master Command Prompt Access Today
Mastering how to open Command Prompt in Windows 10/11 unlocks a world of efficiency. From simple searches to advanced shortcuts, these methods cater to all users. Practice with safe commands, and soon you’ll troubleshoot like a pro.
If you encounter issues, comment below. For more guides on Windows tips, subscribe!






